ABOUT VITRAKVI®
NTRKa GENE FUSION:
An important driver in multiple tumor types1-3
NTRK gene fusions have been found to be the oncogenic driver across 25 adult and pediatric solid tumor types.1-4
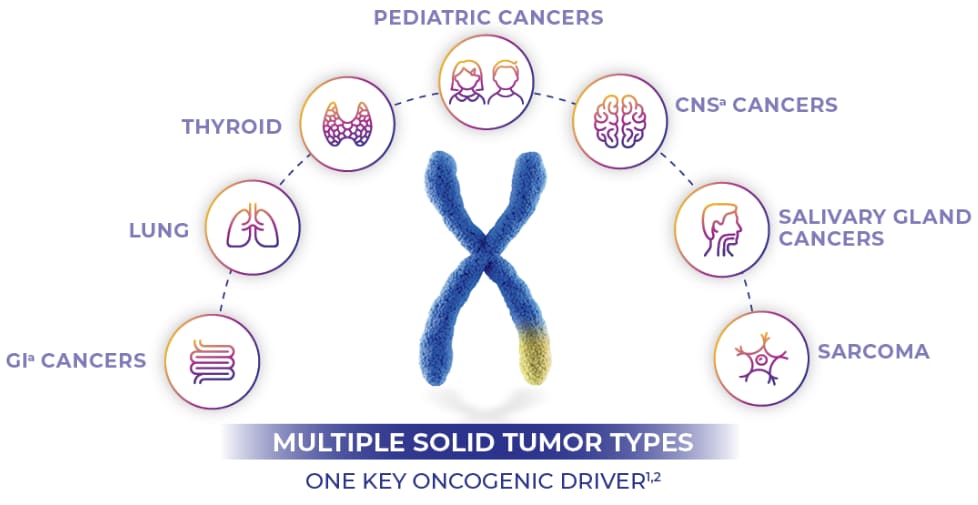

GI CANCERSa

THYROID

LUNG

CNS CANCERSb

SARCOMA

SALIVARY GLAND
CANCERSc

PEDIATRIC CANCERSd
MULTIPLE TUMOR TYPES
ONE KEY ONCOGENIC DRIVER
aCNS, central nervous system; GI, gastrointestinal; NTRK, neurotrophic receptor tyrosine kinase.
NTRK GENE FUSIONS ARE AN IMPORTANT ONCOGENIC DRIVER FOR TRK* FUSION CANCER2,3
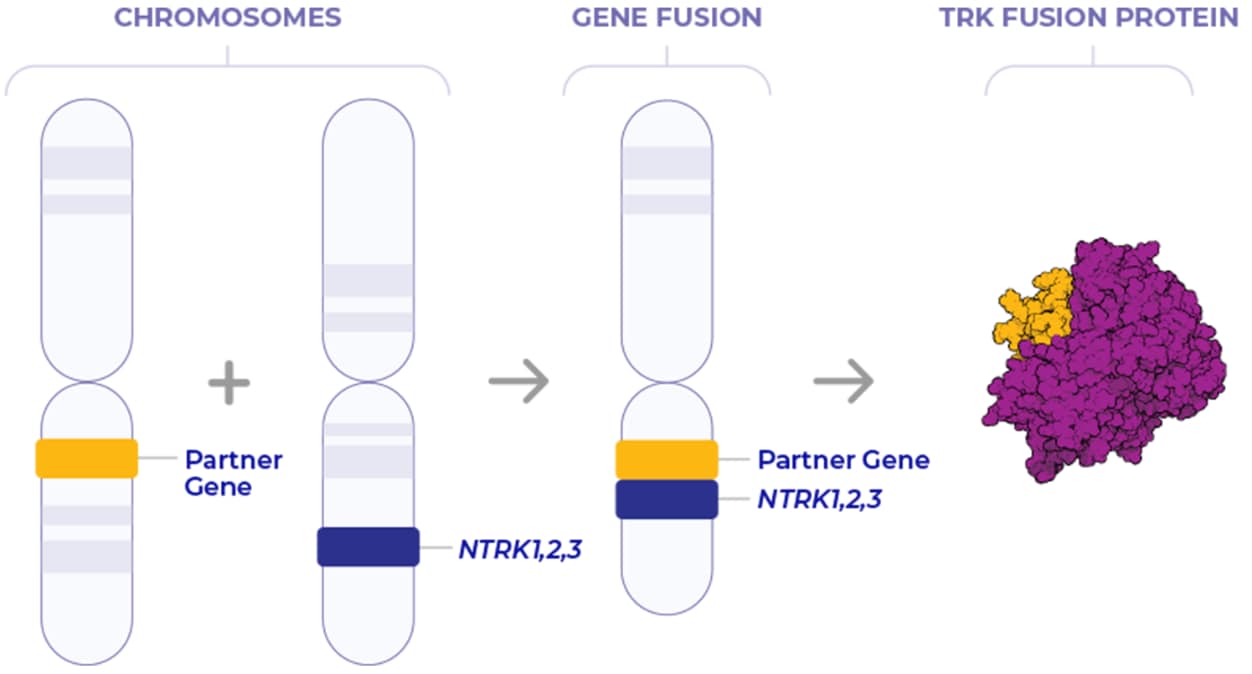
NTRK Gene Fusions Lead to the Formation of Oncogenic TRK Fusion Proteins1
*TRK, tropomyosin receptor kinase.
In TRK fusion cancer, the NTRK gene (NTRK1, NTRK2, and NTRK3) fuses with an unrelated gene.2,5,6
This fusion causes the expression of TRK fusion proteins, which results in cell proliferation and tumor growth.7
VITRAKVI: THE TRK INHIBITOR THAT WAS EXCLUSIVELY DESIGNED TO INHIBIT TRK1
How VITRAKVI works in TRK fusion cancer1
VITRAKVI was exclusively designed to inhibit against the TRK family of proteins (TRKA, TRKB, and TRKC).1
In in vitro and in vivo tumor models, VITRAKVI demonstrated anti-tumor activity in cells with constitutive activation of TRK proteins.1
TRK fusion proteins can act as an oncogenic driver, promoting cell proliferation and survival in tumor cell lines.1
Mechanism of Action: VITRAKVI Exclusively Targets TRK Kinases8
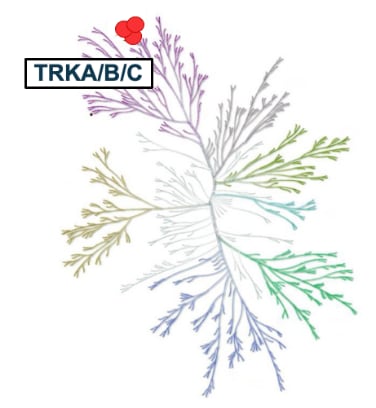
The image above is a depiction of the human kinome, with specific emphasis placed on the TRK family of kinases.8
CNS, central nervous system; GI, gastrointestinal; NTRK, neurotrophic tyrosine receptor kinase; TRK, tropomyosin receptor kinase.
References
- VITRAKVI [package insert]. Whippany, NJ: Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; April 2025. Return to content
- Vaishnavi A, Le AT, Doebele RC. TRKing down an old oncogene in a new era of targeted therapy. Cancer Discov. 2015;5(1):25-34. Return to content
- Okimoto RA, Bivona TG. Tracking down response and resistance to TRK inhibitors. Cancer Discov. 2016;6(1):14-16. Return to content
- Data on file. Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Whippany, NJ. Return to content
- Kumar-Sinha C, Kalyana-Sundaram S, Chinnaiyan AM. Landscape of gene fusions in epithelial cancers: seq and ye shall find. Genome Med. 2015;7:129. doi:10.1186/s13073-015-0252-1. Return to content
- Latysheva NS, Oates ME, Maddox L, et al. Molecular principles of gene fusion mediated rewiring of protein interaction networks in cancer. Mol Cell. 2016;63(4):579-592. Return to content
- Amatu A, Sartore-Bianchi A, Siena S. NTRK gene fusions as novel targets of cancer therapy across multiple tumour types. ESMO Open. 2016;1(2):e000023. doi:10.1136/esmoopen-2015-000023. Return to content
- Brose M, Bauer TM, Burris HA III, et al. LOXO-101, a selective pan-TRK inhibitor for patients with TRK-alterations. Poster presented at: 15th International Thyroid Congress; October 18-23, 2015; Lake Buena Vista, FL. Presentation 386. Return to content